FSC-BT3431 Programming User Guide
Introduction
Description
This guidance document is suitable for engineers developing FSC-BT3431 series Bluetooth modules
Module Default Settings
Name |
FSC-BT3431 |
Service UUID |
FFF0 |
Notify UUID |
FFF1 |
Write UUID |
FFF2 |
UART Baudrate |
115200/8/N/1 |
Hardware Description
Pin Diagram
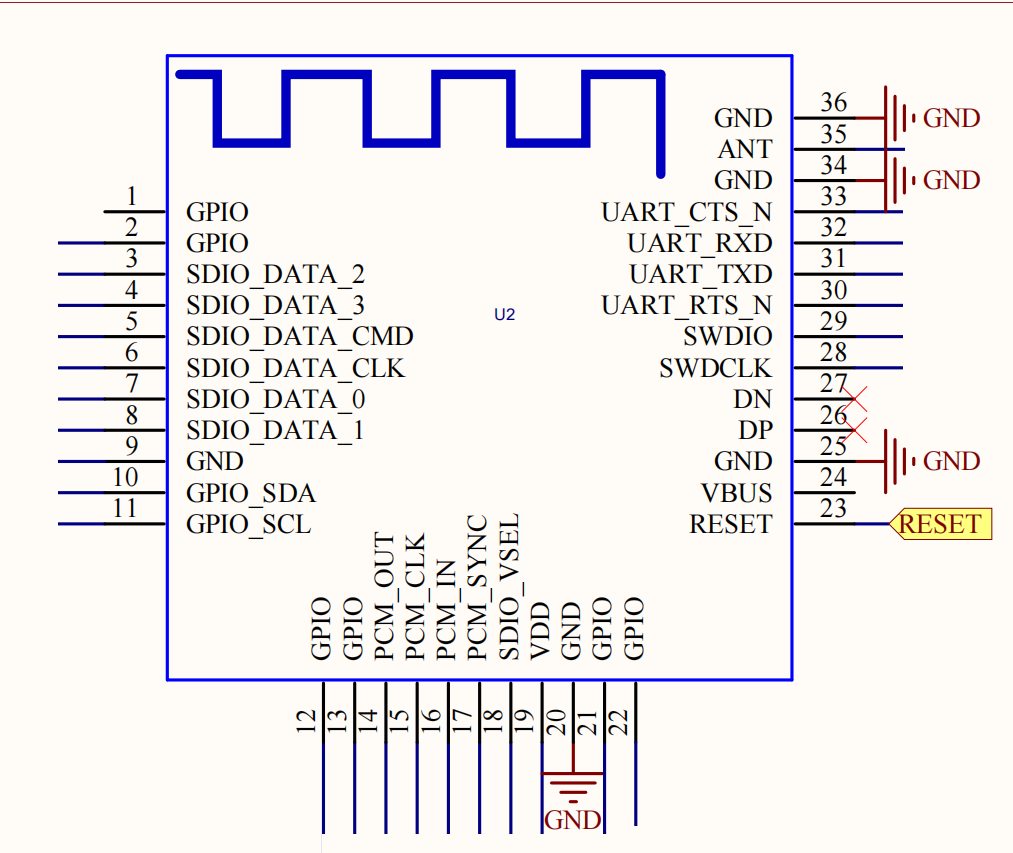
Pin Description
Pin |
Pin Name |
Type |
Pin Descriptions |
|---|---|---|---|
31 |
UART_TX |
O |
UART data output |
32 |
UART_RX |
I |
UART data input |
23 |
RESET |
I |
External reset input: Active LOW, with an inter an internal pull-up. |
20 |
VDD |
Power |
Power supply voltage 3.3V |
21 |
GND |
GND |
Power Ground |
28 |
SWCLK |
I/O |
SWD CLK line(Default) |
29 |
SWDIO |
I/O |
SWD DATA line(Default) |
8 |
SLP_IND |
O |
After Bluetooth connection, the module pulls low to notify the customer’s MCU to exit sleep mode, and outputs
serial data with a delay of 10ms; after Bluetooth disconnection, the module pulls high to notify the customer’s
MCU to enter sleep mode.
|
7 |
WAKE_UP |
I |
MCU pulls high to put the module into sleep mode, and MCU pulls low to wake the module from sleep mode. |
21 |
LED |
O |
Bluetooth not connected output square wave, Bluetooth connection output high level |
22 |
STATUS |
O |
Bluetooth not connected output low level, Bluetooth connection output high level |
Hardware Design Notes
The simple test of the module only needs to connect VDD/GND/UART_RX/UART_TX to use
If the MCU needs to obtain the connection status of the Bluetooth module, it needs to be connected to the STATUS pin(PIN 10)
If the user wants to obtain the working status of the module, they need to connect to the LED pin (pin 21)
If need low power consumption, please connect PIN8 and PIN7
After drawing the schematic diagram, please send it to Feasycom for review, so as to prevent the Bluetooth distance from not reaching the best effect
Function Description
GPIO state
LED PIN is PIN 21
State |
Description |
|---|---|
1Hz square wave |
disconnect state |
high level |
connected state |
Connection status PIN is PIN 22
State |
Description |
|---|---|
low level |
disconnect state |
high level |
connected state |
Mode
Throughput mode |
when disconnected, the data received by the serial port is analyzed according to the AT command;
when connected, all the data received by the serial port is sent to the remote Bluetooth as it is.
|
Command mode |
when disconnected, the data received by the serial port is analyzed according to the AT command;
when connected, The data received by the serial port is still parsed according to the AT command.
When it is necessary to send data to the remote end, send AT+LESEND command.
|
Introduction to Low-Power Mode
Setting up Low-Power Mode
To activate or deactivate the low-power functionality using the command ‘AT+LPM{=Param}’.
Low-power consumption working strategy
AT+LPM=1 |
- When the BT serial port does not receive data for more than 5 seconds, it automatically enters low-power consumption mode
- The first frame of data from the BT serial port wakes up the Bluetooth
- Connection successful, not entering low-power consumption mode.
|
AT+LPM=2 |
MCU pulls high PIN7 to put the BT into sleep mode
MCU pulls low PIN7 to wake up the BT from sleep mode
After Bluetooth connection, the BT pulls low PIN8 to notify the MCU to wake up from sleep mode, and then outputs data with a delay of 10ms
After Bluetooth disconnects, the BT pulls high PIN8 to notify the MCU to enter sleep mode
|
GATT Throughput Service
type |
UUID |
Permissions |
Description |
Service |
0xFFF0 |
GATT Throughput Service |
|
Write |
0xFFF2 |
Write, Write Without Response |
APP send data to module |
Notify |
0xFFF1 |
Notify |
Module send data to remote |
Data transfer rate
Baudrate |
packet size |
interval |
conn interval |
BLE method |
rate |
921600 |
244 |
20ms |
7.5ms |
Notify |
12000 Byte/s |
AT command description
Command description
Throughout this specification:
Content between { } is optional
Content behind << represents a COMMAND from Host
Content behind >> represents a RESPONSE to Host
Command
Command Format
All commands start with “AT”, end with <CR><LF>
<CR> means “carriage return”, corresponds to hex value 0x0D
<LF> means “line feed”, corresponds to hex value 0x0A
If Command has Parameter, Parameter follows behind ‘=’
If Command has multiple Parameters, Parameter must be separated by ‘,’
If Command has Response, Response starts with <CR><LF>, ends with <CR><LF>
Module will always report command’s execution result by using “OK” for success or “ERROR” for failure
Event
Event Format
All Events start with <CR><LF>, end with <CR><LF>
If Event has Parameter, Parameter follow behind ‘=’
If Event has multiple Parameters, Parameter must be separated by ‘,’
Commands Table
AT - Serial communication test
Command |
AT |
Response |
OK |
Description |
When powering on or changing the baud rate, test the UART communication between the host and the module |
AT+VER - Get Firmware Version
Command |
AT+VER |
Response |
+VER=Param |
|
Firmware version |
Description |
Get Firmware Version |
AT+ADDR - Get MAC Address
Command |
AT+ADDR |
Response |
+ADDR=Param |
|
Module’s MAC address (12 Bytes ASCII) |
Description |
Get MAC Address |
AT+NAME - Get/Set Local Name
Command |
AT+NAME{=Param1{,Param2}} |
|
local name(1~29 Bytes ASCII) |
|
MAC address suffix(0/1,default:0)
0: Disable suffix
1: Enable suffix “XXXX” (lower 4 bytes of MAC address) after local name
|
Response |
+NAME=Param |
|
local name |
Description |
Write local name if parameter exist, otherwise read current local name |
AT+BAUD - Get/Set Uart Baudrate
Command |
AT+BAUD{=Param} |
|
baudrate (2400/4800/9600/19200/38400/57600/115200/
230400/460800/921600, default:115200)
|
Response |
+BAUD=Param |
|
baudrate |
Description |
Module will change baudrate to target value immediately |
AT+TXPOWER - Get/Set TX Power
Command |
AT+TXPOWER{=Param} |
|
tx power(-20,-12,-8,-4,-2,-0,2,3,4,6,8 default:8) |
Response |
+TXPOWER=Param |
|
tx power |
Description |
Get/Set TX Power
BT3431 supports a maximum of 8 dB
|
AT+LPM - Get/Set low power config
Command |
AT+LPM{=Param} |
|
low power mode (0/1/2, default: 0)
0: disable
1: enable low power and wake up by UART
2: enable low power and wake up by IO
|
Response |
+LPM=Param |
|
low power mode |
Description |
Get/Set low power config |
AT+ADVIN - Get/Set advertising interval
Command |
AT+ADVIN{=Param} |
|
advertising interval (20~10000 ms, default: 152ms) |
Response |
+ADVIN=Param |
|
advertising interval |
Description |
Get/Set advertising interval |
AT+LECHCNT - Get/Set the maximum number of connections
Command |
AT+LECHCNT{=Param} |
|
Maximum number of connections allowed (1~2, default:1) |
Response |
+LECHCNT=Param |
|
Maximum number of connections allowed |
Description |
A restart is required after setting the maximum number of connections |
AT+IDCFG - Get/Set 8 bytes ID
Command |
AT+IDCFG{=Param} |
|
8 bytes ID |
Response |
+IDCFG=Param |
|
8 bytes ID |
Description |
Get/Set 8 bytes ID. Help users save 8 bytes IDs. |
AT+LEDISC - Disconnect specified connection
Command |
AT+LEDISC{=Param} |
|
index |
Response |
OK |
Description |
Disconnect the bluetooth connection of the specified index |
AT+LECCONN - Initiate a connection to the specified address
Command |
AT+LECCONN{=Param1{,Param2{,Param3{,Param4}}}} |
|
12-byte device address + 1-byte address type |
|
Communication Service UUID |
|
Communication UUID with write/write without rsp permission |
|
Communication UUID with notification permission |
Response |
OK |
Description |
Initiate a connection to the specified device, the parameter consists of 12 bytes (device address) and 1 byte
(address type), generally the address type is “0” or “1”. address
How to get the address type:
Send AT+SCAN=1 command, get parameter2. example:
+SCAN=0,0,DC0D30001ED4,-65,10,FSC-BT946
Connection command:
AT+LECCONN=DC0D30001ED40
|
AT+FILTER - Get/Set scan filter
Command |
AT+FILTER{=Param1{,Param2}} |
|
scan filter (0~3)
0: delete all conditions
1: address filtering
2: advertising data filtering
3: RSSI filtering
|
|
The filter type is 1, and the parameter2 is the address
The filter type is 2, and the parameter2 is advertising data
The filter type is 3, and the parameter2 is RSSI
|
Response |
+FILTER=1,Param1
+FILTER=2,Param2
+FILTER=3,Param3
|
Description |
Filter commands will only affect AT+SCAN=2
When filtering advertising data, the parameter2 fields are: tag, offset, len, data
After the configuration is complete, start AT+SCAN=2 to filter the scanned devices according to the set parameters
AT+FILTER=0, delete all filter conditions.
Filter parameters will not be saved to flash. Do not save when power off.
|
AT+SCAN - SCAN for nearby devices
Command |
AT+SCAN{=Param} |
|
scanning method (0~2)
0: stop scanning
1: Scan nearby devices, filter duplicate addresses, up to 8 devices can be found
2: Scan BLE advertising packets and output original advertising packets, which can be filtered by AT+FILTER command
|
Response |
+SCAN=Param1,Param2,Param3,Param4,Param5,Param6 (AT+SCAN=1 event format)
+SCAN=Param21,Param22,Param23,Param24,Param25,Param26 (AT+SCAN=2 event format)
|
|
list number |
|
MAC Address type (1 byte) |
|
MAC address (12 bytes) |
|
RSSI |
|
Device name length |
|
Device name |
|
MAC Address type (1 byte) |
|
MAC address (12 bytes) |
|
RSSI |
|
advertising packet type |
|
advertising packet length |
|
advertising packet |
Description |
AT+SCAN=1 Commonly used for searching before connecting
AT+SCAN=2 Often used as a Bluetooth gateway to SCAN for nearby Beacon devices
|
AT+TPMODE - Get/Set throughput mode
Command |
AT+TPMODE{=Param} |
|
Throughput mode (0~1, default 1)
0: Command Mode
1: Throughput Mode
|
Response |
+TPMODE=Param |
|
Throughput mode |
Description |
When bluetooth connected and in throughput mode,
the AT command will be de-active,
every byte received via physical UART will be sent to remote.
|
AT+ADVEN - Get/Set advertising enable config
Command |
AT+ADVEN{=Param} |
|
enable (0~1, default 1)
0: disable advertising
1: enable advertising
|
Response |
+ADVEN=Param |
|
enable |
Description |
Trun on/off advertising |
AT+ADVDATA - Get/Set advertising manufacturer specific data
Command |
AT+ADVDATA{=Param} |
|
manufacturer specific data, tag 0xff |
Response |
+ADVDATA=Param |
|
manufacturer specific data, tag 0xff |
Description |
Get/Set advertising manufacturer specific data |
AT+LESEND - send data to remote device
Command |
AT+LESEND{=Param1{,Param2{,Param3}}} |
|
Connection index |
|
data len |
|
data |
Response |
OK |
Description |
send data to remote device |
AT+CHINFO - Get connection list infomation
Command |
AT+CHINFO |
Response |
+CHINFO=Param1,Param2,Param3,Param4 |
|
Connection index |
|
Connection state (1:not connected, 2: connecting, 3: connected) |
|
Connection role (0: peripheral, 1: central) |
|
peer mac address |
Description |
Get connection list infomation |
AT+REBOOT - Soft Reboot
Command |
AT+REBOOT |
Response |
OK |
Description |
Module release all Bluetooth connections then reboot |
AT+RESTORE - Restore Factory Settings
Command |
AT+RESTORE |
Response |
OK |
Description |
Module restore all factory settings then reboot |
Event Table
+SCAN - AT+SCAN=1 Scan Result
Indication |
+SCAN=Param1,Param2,Param3,Param4,Param5,Param6 |
|
Index |
|
MAC address type (1 byte) |
|
MAC address (12 Bytes ASCII) |
|
RSSI |
|
remote device name len |
|
remote device name |
Description |
After the module receives AT+SCAN=1, it will continue to scan, and report through +SCAN after finding the device |
+SCAN - AT+SCAN=2 Scan Result
Indication |
+SCAN=Param1,Param2,Param3,Param4,Param5,Param6 |
|
MAC address type (1 byte) |
|
MAC address (12 Bytes ASCII) |
|
RSSI |
|
advertising packet type |
|
advertising packet size |
|
advertising packet(For ease of MCU reading, the data is in hexadecimal format. Please set the serial port display to hexadecimal mode to avoid displaying garbled text.) |
Description |
After the module receives AT+SCAN=2, it will continue to scan and report through +SCAN after finding the device |
+GATTSTAT - GATT State
Indication |
+GATTSTAT=Param1,Param2 |
|
Connection Index |
|
GATT State (1~3)
1: Standby
2: Connecting
3: Connected
|
Description |
In the command mode, if the connection status of the module changes, it will be actively reported through +GATTSTAT |
+DATA - GATT Received Incoming Data
Indication |
+DATA=Param1,Param2,Param3 |
|
Index |
|
Payload length |
|
Payload |
Description |
In the throughput mode: report data without +DATA header
In the command mode: report data with +DATA header +DATA=1,5,12345
|
Application scenarios
Get/Set the default parameters of the module
When the module is disconnect state, it will parse the uart data according to the AT command. The host can get and set the default parameters of the module, as shown in the figure below:
Set the device name to ABC
Get device name
Get MAC address
Process of sending data
When the module is powered on, it will continue to send advertising data, and the remote device (mobile phone) can scan the advertising packet. And initiate a connection request to the module. After the connection is successful, the module will pull up the connection status pin to notify the host that the Bluetooth connection is successful. The host can send data to the remote device through the Bluetooth module, and the remote device can also send data to the host.
The module acts as the central to connect to the remote device
The module can be used as a master device to connect to the slave device, and the host can send commands to control the module to scan and connect and disconnect. The figure below shows the process of connecting other devices:
FAQ
How does an IOS mobile phone scan the Bluetooth MAC address?
For security reasons, the IOS system converts the Bluetooth MAC address into a UUID at the bottom layer and sends it to the upper layer application. Therefore, the APP cannot get the MAC address of the device.
FSC-BT3431 will put the MAC address in the advertising packet by default, and the APP can get the MAC address from the advertising packet through the following methods.
- (void)centralManager:(CBCentralManager *)central didDiscoverPeripheral:(CBPeripheral *)peripheral advertisementData:(NSDictionary *)advertisementData RSSI:(NSNumber *)RSSI { if(![self describeDictonary:advertisementData]) { NSLog(@"is not fsc module"); return; } } - (Boolean)describeDictonary: (NSDictionary *) dict { NSArray *keys; id key; keys = [dict allKeys]; for(int i = 0; i < [keys count]; i++) { key = [keys objectAtIndex:i]; if([key isEqualToString:@"kCBAdvDataManufacturerData"]) { NSData *tempValue = [dict objectForKey:key]; const Byte *tempByte = [tempValue bytes]; if([tempValue length] == 6) { // The parameter after tempByte is the Bluetooth address return true } }else if([key isEqualToString:@"kCBAdvDataLocalName"]) { //there is name //NSString *szName = [dict objectForKey: key]; } } return false; }