Development Examples
Data Throughput Mode Application
What is Throughput Mode?
FSC-BT3721V Bluetooth BLE data module has two work modes: Throughput Mode and Command Mode .
The generic data throughput firmware for the FSC-BT3721V modules defaults to throughput mode. To switch modes, refer to FSC-BT3721V General Data AT Command Set and use AT+TPMODE command. The differences between the two work modes are as follows:
Throughput Mode :
Bluetooth Not Connected : Data received via UART is parsed as AT commands.
Bluetooth Connected : All data received via UART is sent as-is to the remote Bluetooth device. It does not contain any data headers or framing and does not require AT commands to send data.
Command Mode :
Bluetooth Not Connected : Data received via UART is parsed as AT commands.
Bluetooth Connected : Data received via UART is still parsed as AT commands. It will contain specific response indication headers and framing. Data must be sent to the remote device using AT commands, such as AT+LESEND .
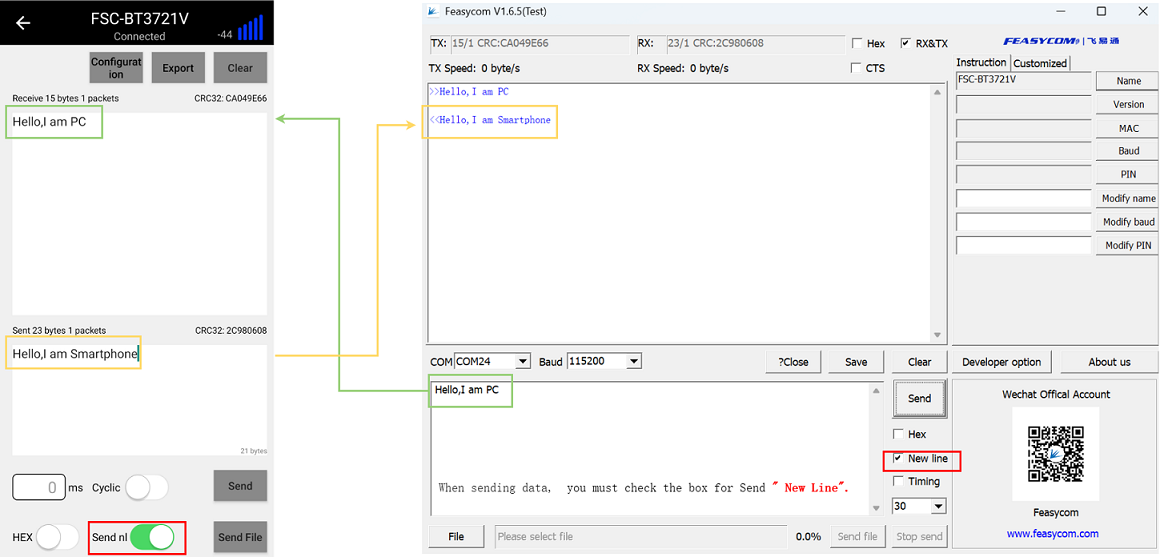
Module to Phone Application
1.Module Side: After power-on, the module will continuously send broadcast packet data;
2.Mobile Phone Side: Open the [FeasyBlue App] , scan for broadcast packets of nearby Bluetooth BLE devices, find the target Bluetooth module, and establish a connection;
3.After successful connection, the status pin of the module will pull up the level, indicating that the connection has been established;
4.After successful connection, in throughput mode, the module will automatically transmit the serial port data it receives to the remote end (mobile phone side) via air.
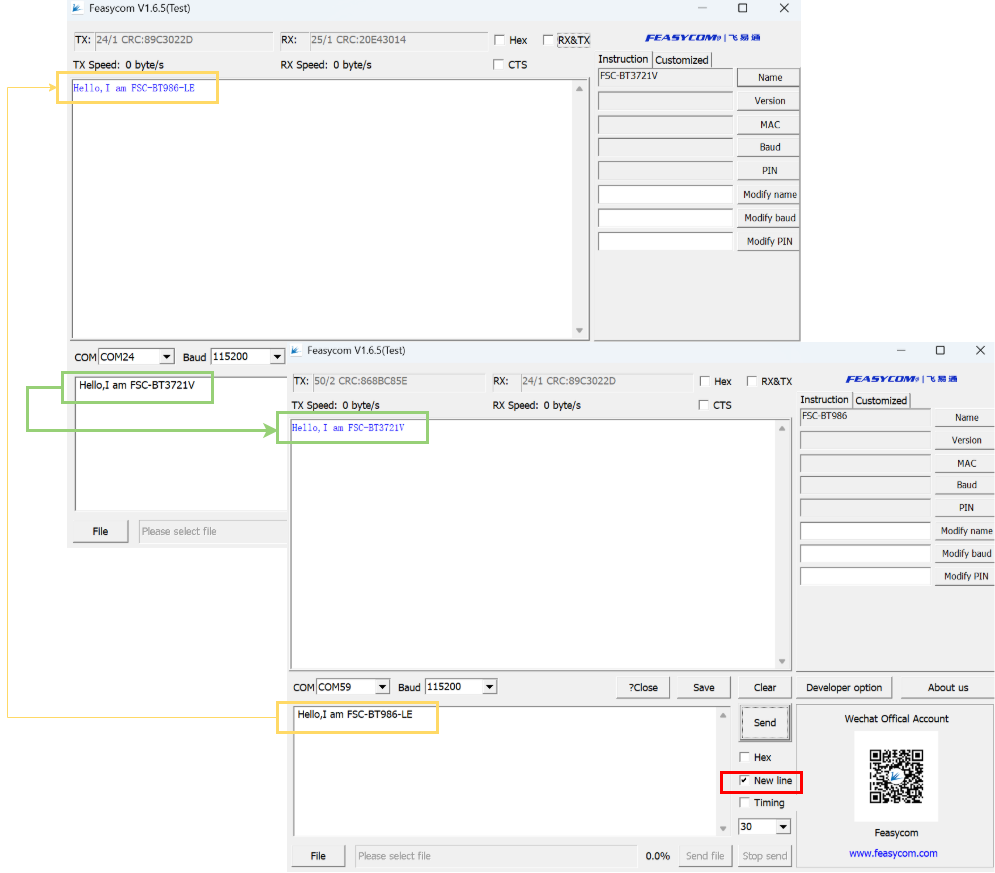
Module to Module Application
Demonstration of BLE communication data throughput transmission between FSC-BT3721V and FSC-BT986-LE Bluetooth modules, as follows:
1.Scan for nearby BLE devices
FSC-BT3721V Scan for nearby Bluetooth BLE devices.
1Send:<<AT+SCAN=1 //Scan for nearby Bluetooth BLE devices
2Response:>>OK
3 >>+SCAN={ //Scan Started
4 >>+SCAN=0,1,DD0D3053CBED,-66,19,iMin TF2-34 LE CBED
5 >>+SCAN=1,0,DC0D3060D2E9,-68,12,FSC-BW236-LE
6 >>+SCAN=2,0,DC0D30001106,-76,12,FSC-BT1106RC
7 >>+SCAN=3,0,DC0D300017A9,-87,11,FSC-BT3721V
8 >>+SCAN=4,1,DD0D3000174C,-13,12,FSC-BT986-LE //The target module's MAC address and address type 1 are identified.
9 >>+SCAN=} //Scan Completed
2.Establish BLE connection request
FSC-BT3721V eestablish BLE protocol connection with FSC-BT986-LE via the AT+LECCONN command. Operation is as follows:
1Send: <<AT+LECCONN=DD0D3000174C1 //Establish BLE connection request
2Response: >>OK
Warning
AT+LECCONN=Target Bluetooth MAC address + 1-bit address type. Generally, the address type is “0” or “1”.
How to obtain the address type:
Use the AT+SCAN=1 command to scan, the second parameter in the returned result is the address type, as shown in the example below:
1 //The address type is the second parameter, which is "1".
2
3 Response: >>+SCAN=4,1,DD0D3000174C,-13,12,FSC-BT986-LE
3.BLE Connection Established Successfully
In throughput mode, after the Bluetooth connection is successfully established, the serial port cannot receive event response indicators. The current connection status can be determined by the level state of Pin8 (status indicator pin) of FSC-BT3721V, as detailed below:
High Level (H): Indicates Bluetooth is successfully connected.
Low Level (L) : Indicates Bluetooth is not connected or the connection has been disconnected.
4.Send Data
The throughput mode of the general data transmission firmware is enabled by default. After BLE connection is successfully established, data can be sent directly without the need to send data via AT commands.
Read/Write Module Default Parameters
When Bluetooth is not connected, the module parses UART data as AT commands. The host can query and modify the module’s default parameters. The following example demonstrates:
Write Device Name : ABC
Read Device Name
Read Bluetooth Address
Data Transmission Flow
1.When the module is powered on, it continuously sends broadcast data outward. A remote Bluetooth device (e.g., a mobile phone) can obtain the broadcast packet by searching and initiate a connection request to the module.
2.After the connection is successfully established, the module will pull high the connection status pin to notify the host that the Bluetooth connection has been successfully established.
3.The host can send data to the remote Bluetooth device via the Bluetooth module, and the remote Bluetooth device can also send data to the host.
Module Acts as Master to Connect to Remote Device
The module can act as master device to connect to remote slave devices.
The host can send AT commands to control the module to perform scanning, connection, and disconnection operations. The following shows the process of connecting to other devices: